Always refer to the main Pearson general guidelines when writing alternative text for images.
To further assist you when describing maps, here are some key aspects to keep in mind followed by examples. Not all guidance will apply to all images.
- Begin with a clear and concise summary: Start your description with a summary of the map’s purpose and main features. Avoid alt text that only states, “A map.”
- Provide a detailed description of the map’s features: Once you have provided a summary, most maps will need a long description to fully describe it. Begin by describing the map’s key features in detail. Make sure to only include important details needed to understand the meaning of the map. For example, if it is a map of a city, you may want to describe the major landmarks, streets, and neighborhoods. If it is a topographical map, you may want to describe the elevation changes and natural features such as rivers and mountains.
- Use clear and descriptive language: Use clear and descriptive language to describe the map’s features. Avoid using technical jargon or complex vocabulary that may be difficult for users to understand.
- Provide context: Provide context for the map’s features by including information about the time, location, and purpose of the map. This will help readers understand the significance of the map and its features.
- Include relevant statistics and data: If the map includes statistics or data, be sure to include this information in your description. This can help users understand the information presented on the map and its relevance to their needs.
- Use visual cues: Use visual cues such as arrows or labels to help readers identify specific features on the map. This can be particularly helpful when describing complex or detailed maps.
- Consider the surrounding text: Do not repeat information placed in it to support the map. Repeating this information is redundant and provides a poor user experience.
Examples
Reminder: The Mastering authoring platform has a title field and alt text field but does not have the functionality for a long description. Alternative text descriptions in Mastering may have more than 255 characters. The eText 2 authoring platform has the functionality for alt text and a long description. For more information about the different authoring systems, see Platform Authoring Information.
Example 1
Alt Text
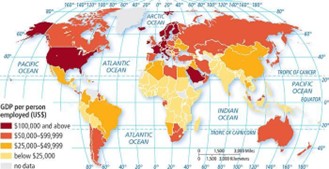
A thematic map of the world depicting the distribution of G D P per person employed in U S dollars.
Long Description
(Must be marked up in HTML)
The map’s scale is 1 unit equals 1,500 miles. The distribution is as follows:
100,000 dollars and above:
- Northwestern Europe: Ireland and Denmark.
- Northern Europe: Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
- Southern Europe: Italy and Malta.
- Western Europe: France, Germany, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Austria, and Belgium.
- Western Asia: The United Arab Emirates.
- Southwestern Asia: Qatar and Saudi Arabia.
- In the northwest of North America: The United States including Alaska.
- To the southeast of the U S in North America: Puerto Rico.
50,000 to 99,999 dollars:
- In the northern region of North America: Canada.
- In Central America: Costa Rica and Panama.
- On the southeastern coast of the U S in North America: the Bahamas.
- Northern Europe: The United Kingdom, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Slovakia.
- Eastern Europe: Poland, Romania, Czechia, and Hungary.
- Southeastern Europe: Bulgaria and Greece.
- Southern Europe: Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia, and Herzegovina.
- Southwestern Europe: Spain and Portugal.
- Western Asia: Cyprus and Turkey.
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan and Russia.
- Eastern Asia: South Korea and Japan.
- Southeastern Asia: Malaysia.
- Southern Asia: Iran.
- Southwestern Asia: Oman.
- Australia: Australia.
- To the southeast of Australia: New Zealand.
- Northern Africa: Libya.
- Central Africa: Gabon and Equatorial Guinea.
- Southern Africa: South Africa and Botswana.
- In the southern regions of South America: Chile, Argentina, and Uruguay.
- On the northern mainland of South America: Guyana.
25,000 to 49,999 dollars:
- In the southern portion of North America: Mexico.
- In the southeastern region of North America: Haiti.
- Eastern Europe: Belarus and Ukraine.
- In the northwest of South America: Colombia.
- In the east of South America: Suriname.
- In the northeast of South America: Brazil.
- In the southeastern region of South America: Paraguay.
- Northern Africa: Morocco, Algeria, Egypt, and Tunisia.
- Southern Africa: Namibia.
- Western Asia: Iraq, Jordan, Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan.
- Eastern Asia: China and Mongolia.
- Southeastern Asia: Thailand.
- Southern Asia: Sri Lanka.
Below 25,000 dollars:
- Central Asia: Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan.
- Eastern Asia: Taiwan and North Korea.
- Southeastern Asia: Myanmar, Laos, Singapore, Philippines, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia.
- Southern Asia: Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
- Eastern Africa: Burundi, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya.
- Southeastern Africa: Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, Somalia, and Comoros.
- Southern Africa: Zambia, Zimbabwe, Eswatini, and Lesotho.
- Middle Africa: Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Democratic Republic Congo, Sao Tome & Principe.
- Western Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Cote d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Niger, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
- Northwestern Africa: Mali, Mauritania, and Senegal.
- In the western region of South America: Bolivia.
- In the northwestern region of South America: Peru and Ecuador.
- In the northwest of South America (in Central America): Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua.
No data:
- In the northeast of North America: Greenland.
- Western Asia: Yemen.
- Central Asia: Turkmenistan.
- In the northwest of Africa: Western Sahara.
- Middle Africa: South Sudan.
- In the north of South America: Venezuela.
Example 2
Alt Text
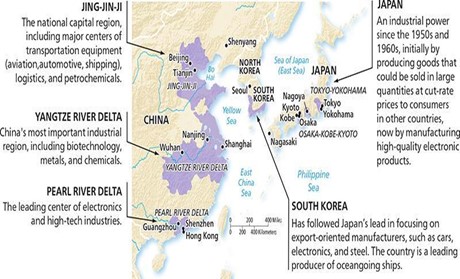
A map of East Asia depicting its industrial regions.
Long Description
(Must be marked up in HTML)
The map’s scale is 1 unit equals 200 miles. The major industrial regions of East Asia are as follows:
- In the northwestern region within Eastern Asia: Jing-Jin-Ji. The national capital region, including major centers of transportation equipment (aviation, automotive, shipping), logistics, and petrochemicals. It includes the cities of Beijing and Tianjin.
- In the northeastern region within Eastern Asia: Japan. Japan is an industrial power since the 1950s and 1960s, initially by producing goods that could be sold in large quantities at cut-rate prices to consumers in other countries, now by manufacturing high-quality electronic products. It includes Tokyo-Yokohama, Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto, and Nagoya.
- In the eastern region within Eastern Asia: South Korea. South Korea has followed Japan’s lead in focusing on export-oriented manufacturers, such as cars, electronics, and steel. The country is a leading producer of oceangoing ships. It includes the southern coast of South Korea.
- In the southern region within Eastern Asia: The Pearl River Delta. The leading center of electronics and high-tech industries. This region includes the cities of Guangzhou, Hong Kong, and Shenzhen.
In the central western region within Eastern Asia: The Yangtze River Delta. China’s most important industrial region, including biotechnology, metals, and chemicals. This region includes the cities of Wuhan, Nanjing, and Shanghai.
Dated: 2023-12-01
