Always refer to the main Pearson general guidelines and science guidance when writing alternative text for images.
When describing images of magnification, keep in mind the following key aspects and examples. Not all guidance will apply to all images.s.
- If relevant for understanding, start by identifying the type of scan or image. For example, “Microscopic image of a cross-section of a leaf.”
- Describe meaningful labels and magnification levels displayed in the image.
- Use the word “times” when referring to total magnification. For example, “Seen at 400x” would be written as “Seen at 400 times.”
- If describing ocular and objective lenses, use “X” instead of the word “times”. For example, 10x would be written as “10 X” because the language is more natural.
- Identify the image features that relate to the concept being represented or the question being asked. This may include structures, patterns, colors, or other relevant details. Be concise and descriptive, using precise scientific terminology from the main text.
Examples
Reminder: The Mastering authoring platform has a title field and alt text field but does not have the functionality for a long description. Alternative text descriptions in Mastering may have more than 255 characters. The eText 2 authoring platform has the functionality for alt text and a long description. For more information about the different authoring systems, see Platform Authoring Information.
Example 1

Alt Text
A micrograph of a lymphatic vessel and valve taken by a light microscope at 63 times magnification.
Long Description
(Must be marked up in HTML)
In the micrograph, the lymphatic vessel appears as a horizontal pipe like structure that contains the lymphatic valve. Like valves in veins, each lymphatic valve consists of a pair of flaps that permit movement of fluid in only one direction.
Example 2
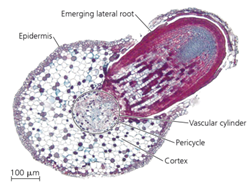
Alt Text
A light micrograph at a scale of 100 micrometers shows a cross section of an original root. An emerging lateral root starts in the vascular cylinder, then pushes out through the pericycle, cortex, and epidermis.
Example 3
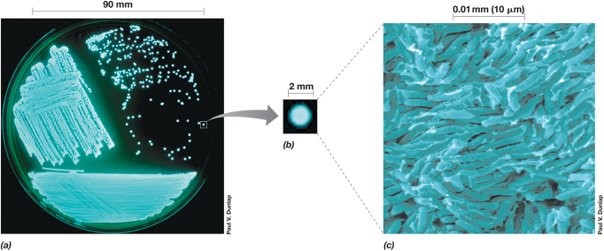
Alt Text
A 3 part diagram shows bioluminescent bacteria colonies at different scales.
Long Description
(Must be marked up in HTML)
Parts A, B, and C show the bacteria colonies at increasingly small scales. In each part, the bacteria appear to glow pale blue.
- Part A. The bacteria colonies appear as scattered dots in a petri dish 90 millimeters in diameter.
- Part B. A single bacteria colony appears as a smooth disk approximately 2 millimeters in diameter.
- Part C. At a scale of 0.01 millimeters or 10 micrometers, individual bacteria are rod shaped, with roughly hemispherical ends.
Example 4
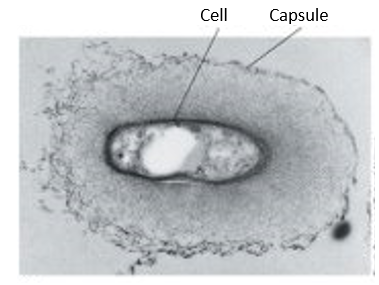
Alt Text
A grayscale micrograph shows a cell inside a capsule. The cell is roughly oval with a solid dark gray boundary. The capsule is also roughly oval. Its outer boundary appears stippled in light to medium gray.
Dated: 2023-12-01
